Address:
20 Park Plaza, Suite 804
Boston, MA 02116
978-888-7999
Address:
20 Park Plaza, Suite 804
Boston, MA 02116
978-888-7999

The longer we study vitamin D, the more benefits we find. Below is a chart of diseases affected by Vitamin D (the degree of influence is decidedly optimistic.)

In a study of nine countries published online, those with low vitamin D had a 16% greater risk of severe COVID-19. In a study in the Irish Medical Journal, people in Norway, Sweden, and Finland, where food is supplemented and vitamin D levels are high, had a lower infection rate and lower mortality rate than Europeans living in Spain and Italy. However, a study published in Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome found no correlation between vitamin D and COVID-19 infection risk in Britain. However, that was early in their COVID-19 epidemic.
The notion of a “healthy” level of vitamin D has changed remarkably over the years. 25 years ago, normal vitamin D level was 14 to 28 IU, with toxicity thought to start at 50. However, the current normal vitamin D level is between 30 and 50, and toxicity is 100. In other words, evidence now supports a doubling in dose.
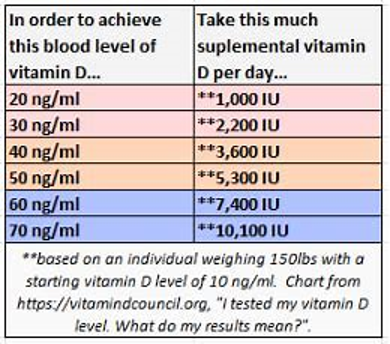
How much vitamin D should you take to obtain a healthy level? The following chart is a guideline. Since there is a fair amount of variation from one individual to the next, I strongly recommend getting a vitamin D level test. Many factors – sunlight, diet, and supplements – influence the total vitamin D in the body. Medical specialty societies recommend significantly lower numbers. Discuss this with your doctor.
British physicians, however, published an opinion in the British Medical Journal that taking high doses of vitamin D had no effect on COVID-19. This is quite curious coming from a country where one out of five people is vitamin D deficient, less than 2% of the population gets tested for vitamin D levels, and public policy is to take vitamin D supplements. The devil is in the details – the British recommended daily dose of supplemental vitamin D is 4000 units, which by international standards, is a high dose!
The conclusion: this is supportive evidence for maintaining levels of vitamin D in the 40-50 range in the age of COVID-19. It adds yet another reason to the evidence for the other benefits of vitamin D.
These drugs lower cholesterol. The most widely known is Lipitor. Researchers in Belgium reported among 154 nursing home patients, those taking a statin were three times more likely to be free of symptoms during an active COVID-19 infection. They were also less likely to need hospitalization or die. Should all nursing home patients be on a statin? Perhaps if the statin had very few side effects. The first statin – Pravachol – has the best safety profile and least side effects.
COVID-19 binds to the hemoglobin molecule in red blood cells and increases blood clotting and inflammation. This inflammation affects primarily the lungs, but also the brain, heart, liver, and kidneys. Patients in intensive care units had rapid clotting of their IV lines as well as spontaneous blockages in other areas of the body. Administration of blood thinners improved patient outcomes and decreased intensive care unit stays. The drugs administered in these circumstances are 1000 times more powerful anticoagulant than aspirin. If you have an indication for taking aspirin, such as a recent heart attack, you should continue to do so. This research does not in any way indicate you should start taking aspirin to prevent COVID-19 complications.